While doing business, raising invoices is a day-to-day work and its accounting is also an essential part to smoothly run business. You might have not thought that there is any method or rule to issue an invoice or how an invoice should be under GST to avoid any penalty from the tax authorities.
But, I tell you that the CGST Rules has outlined the method to generate invoice and what fields should be included. In this post, I will discuss all important parameters that an invoice should determine whether it is a sale invoice or export invoice.
Rule 46 of the CGST Rules 2017
A Tax invoice shall be issued by the registered person containing the following particulars, namely,-
(a) name, address and Goods and Services Tax Identification Number of the supplier;
(b) a consecutive serial number not exceeding sixteen characters, in one or multiple series, containing alphabets or numerals or special characters- hyphen or dash and slash symbolized as ―-‖ and ―/‖ respectively, and any combination thereof, unique for a financial year;
(c) date of its issue;
(d) name, address and Goods and Services Tax Identification Number or Unique Identity Number, if registered, of the recipient;
(e) name and address of the recipient and the address of delivery, along with the name of the State and its code, if such recipient is unregistered and where the value of the taxable supply is fifty thousand rupees or more;
(f) name and address of the recipient and the address of delivery, along with the name of the State and its code, if such recipient is unregistered and where the value of the taxable supply is less than fifty thousand rupees and the recipient requests that such details be recorded in the tax invoice;
(g) Harmonised System of Nomenclature code for goods or services;
(h) description of goods or services;
(i) quantity in case of goods and unit or Unique Quantity Code thereof;
(j) total value of supply of goods or services or both;
(k) taxable value of the supply of goods or services or both taking into account discount or abatement, if any;
(l) rate of tax (central tax, State tax, integrated tax, Union territory tax or cess);
(m) amount of tax charged in respect of taxable goods or services (central tax, State tax, integrated tax, Union territory tax or cess);
(n) place of supply along with the name of the State, in the case of a supply in the course of inter-State trade or commerce;
(o) address of delivery where the same is different from the place of supply;
(p) whether the tax is payable on reverse charge basis; and
(q) signature or digital signature of the supplier or his authorized representative
(r) [Quick Response code, having embedded Invoice Reference Number (IRN) in it, in case invoice has been issued in the manner prescribed under sub-rule (4) of rule 48]105.
[Provided that the Board may, on the recommendations of the Council, by notification, specify-
(i) the number of digits of Harmonised System of Nomenclature code for goods or services that a class of registered persons shall be required to mention; or
(ii) a class of supply of goods or services for which specified number of digits of Harmonised System of Nomenclature code shall be required to be mentioned by all registered taxpayers; and
(iii) the class of registered persons that would not be required to mention the Harmonised System of Nomenclature code for goods or services:
Provided also that in the case of the export of goods or services, the invoice shall carry an endorsement ―SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT/SUPPLY TO SEZ UNIT OR SEZ DEVELOPER FOR AUTHORIZED OPERATIONS ON PAYMENT OF INTEGRATED TAX‖ or ―SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT/SUPPLY TO SEZ UNIT OR SEZ DEVELOPER FOR AUTHORIZED OPERATIONS UNDER BOND OR LETTER OF UNDERTAKING WITHOUT PAYMENT OF INTEGRATED TAX‖, as the case may be, and shall, in lieu of the details specified in clause (e), contain the following details, namely,- (i) name and address of the recipient; (ii) address of delivery; and (iii) name of the country of destination:
Provided also that the signature or digital signature of the supplier or his authorized representative shall not be required in the case of issuance of an electronic invoice in accordance with the provisions of the Information Technology Act, 2000 (21 of 2000)
Read More: Consider these factors for claiming Credit under GST Act
Explanation of the tax invoice
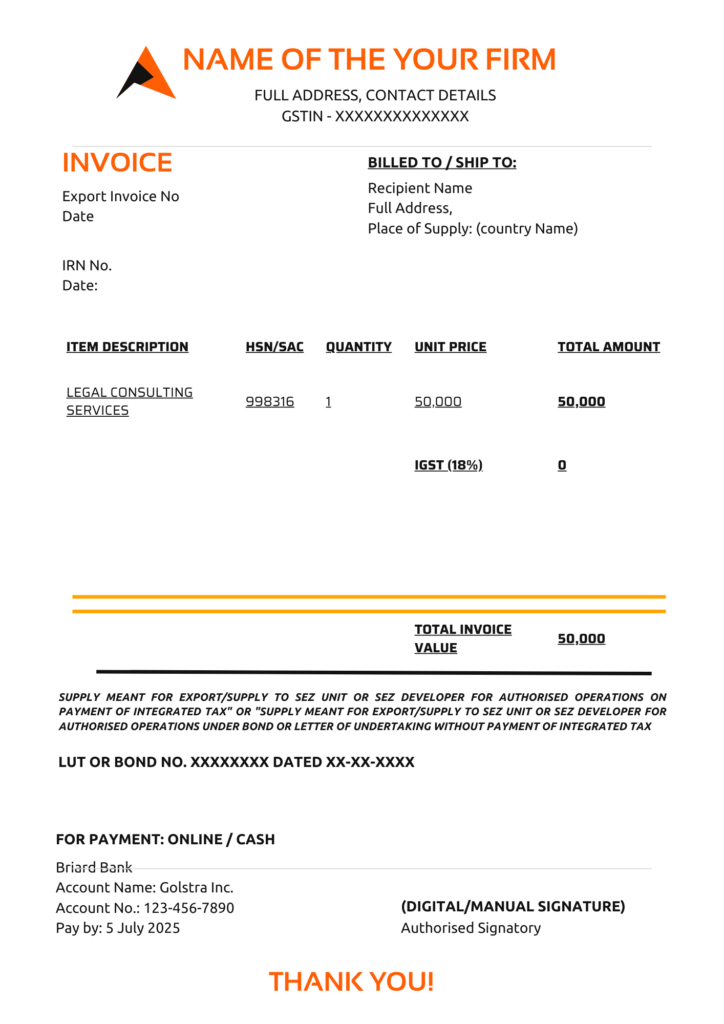
You can analyze Rule 46 which has clearly specified all the parameters should be included in a tax invoice and also how an export invoice should be.
- You have to compulsory mention your Name, GSTIN, Address and the same details of your supplier.
- Do mention the place of supply or state code to know whether you have to charge IGST or CGST/SGST on taxable value
- Taxable Value is the price of your services or goods.
- Invoice Value is Taxable Value + Tax amount (IGST or CGST/SGST)
- Must include Description of goods or services with HSN and each unit price.
- The rate of tax should explicitly be mentioned and also the tax amount calculated on taxable value. You have to mention the total invoice value on the invoice.
- Your signature on the invoice should be there.
- For export invoice, always mention LUT or Bond No with date or IGST amount, whatever is applicable. Always mention this para -”SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT/SUPPLY TO SEZ UNIT OR SEZ DEVELOPER FOR AUTHORIZED OPERATIONS ON PAYMENT OF INTEGRATED TAX‖ or ―SUPPLY MEANT FOR EXPORT/SUPPLY TO SEZ UNIT OR SEZ DEVELOPER FOR AUTHORIZED OPERATIONS UNDER BOND OR LETTER OF UNDERTAKING WITHOUT PAYMENT OF INTEGRATED TAX”. So it can be distinguished for which export invoice has been raised.

Does wrong invoice attracts penalty
Yes, a tax officer can impose a penalty of maximum 50,000 rupees. Section 125 of the CGST Act 2017, empowers the officer to impose a penalty of Rs. 25,000 each under CGST and SGST (max Rs. 50,000) for violating any provision, rules outlined in the CGST Act, or Rules.
I have provided the template for a sample tax invoice which you can refer and use for your business to raise the right invoice as per GST Rules only.










Leave a Reply
View Comments